Which woods are antibacterial?
If you’ve ever wondered what type of cutting board is best for your kitchen from a hygiene perspective, you may want to know which woods are antibacterial.
Although synthetic materials, such as plastic or stainless steel, may seem easier to clean, research suggests that certain woods possess natural antibacterial properties that make them ideal allies for food safety.
Next, we’ll explore the antibacterial properties of the most commonly used woods for cutting boards, with a special emphasis on oak, which has been shown to be one of the most effective types of wood at eliminating bacteria.
Why is wood antibacterial?
Wood contains natural compounds, such as tannins and resins, that make it difficult for harmful bacteria to survive on its surface.
Furthermore, its porous structure creates an unsuitable environment for the proliferation of bacteria.
Unlike plastic materials, where bacteria can accumulate in cut marks, wood tends to “encapsulate” and isolate microorganisms, reducing their ability to multiply.
Oak: the wood with antibacterial properties
If you’re wondering which woods are antibacterial, among the different woods available, oak has positioned itself as one of the safest and most effective options.
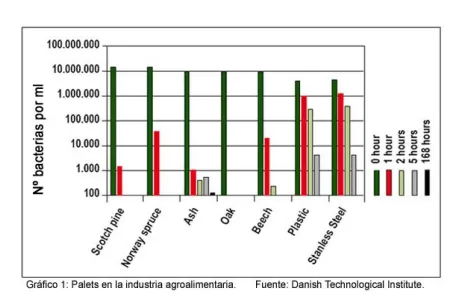
According to research conducted by the Danish Institute of Technology, oak boards can significantly eliminate harmful bacteria inoculated after cleaning with pressurized water.
This study revealed that, compared to plastics or stainless steel, oak achieves a much faster and more efficient reduction in the number of bacteria present on its surface. No wonder this wood has historically been used for a multitude of food-related applications.
Why is oak so effective?
- Natural tannins: Oak contains a high percentage of tannins, which act as powerful antimicrobial agents.
- Porous structure and compact fiber: The density of its grain and its controlled porosity allow bacteria to be “trapped” inside, where they end up dying due to lack of ideal conditions.

Other recommended woods for your cutting boards
Although oak shines for its effectiveness, it is not the only wood with outstanding antibacterial qualities. Other alternatives also offer food safety and durability:
- Maple: With a close grain and moderate hardness, it is one of the favorite woods in professional kitchens. Its fine pores make it difficult to retain moisture and bacteria.
- Iroko: This African wood is known to be similar to Burmese teak. Extremely resistant to weathering and moisture, it is recommended for boards that will be in recurrent contact with wet food. Due to its coarse pore to grain, regular hydration and maintenance is recommended.
- Walnut: In addition to its dark, elegant aesthetics, walnut has natural antimicrobial properties that help keep the surface more hygienic.


Care and maintenance: key to hygiene
The choice of wood is important, but equally or more important is the care you take of your cutting board:
- Immediate washing: After each use, wash the board with hot water and mild soap, removing food residues.
- Complete drying: Allow the board to air dry in an upright position. A damp surface encourages microbial growth.
- Regular oiling: Apply mineral or specific oil for cutting boards to keep the wood nourished and “sealed”, prolonging its useful life and antibacterial properties.
Conclusion on which woods are antibacterial
When it comes to hygiene and food safety in your kitchen, wooden cutting boards offer a natural defense against bacteria that many don’t expect.
Far from being an obsolete material, wood has intrinsic biological advantages that make it an excellent ally compared to other materials such as plastic or stainless steel.
Choosing a board made of oak, maple, beech, or walnut, and caring for it properly, will ensure a safer and healthier environment for your cooking.
Recommended reading on which woods are antibacterial:
- Summary of the study carried out by the Danish Technological Institute : Here
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
What does it mean for wood to be antibacterial?
Antibacterial wood has natural properties that inhibit the growth and proliferation of bacteria on its surface. This is due to components such as tannins and lignin, which act as antimicrobial agents. These properties make certain woods ideal for environments where hygiene is essential, such as kitchens and hospitals.
What types of wood have antibacterial properties?
Some woods recognized for their antibacterial properties include:
- Pine: Contains natural extracts that limit the growth of bacteria and fungi.
- Acacia: Its resistance to moisture and antibacterial properties make it suitable for kitchen utensils.
- Olive: Known for its natural resistance to moisture and bacteria, it is common in cutting boards and utensils.
- Bamboo: Although technically a grass, bamboo has antibacterial properties and is less porous than other woods.
How do the antibacterial properties of wood work?
The porous structure of wood allows bacteria to be absorbed and trapped inside, where they die due to the lack of nutrients and the action of natural antimicrobial compounds present in the wood.
Are wooden cutting boards more hygienic than plastic ones?
Yes, studies have shown that bacteria have a lower survival rate on wooden surfaces compared to plastic ones. While bacteria can multiply on plastic boards, they are absorbed and eliminated more quickly on wooden ones.
What care does antibacterial wood require?
To maintain the antibacterial properties of wood:
- Cleaning: Wash with warm soapy water after each use.
- Drying: Dry completely to avoid moisture build-up.
- Maintenance: Periodically apply food-safe mineral oil to preserve the wood and prevent cracking.
Is it safe to use wooden utensils in the kitchen?
Yes, wooden utensils are safe and, thanks to their antibacterial properties, can be more hygienic than utensils made of other materials. However, it’s important to maintain good hygiene and replace them if they show deep cracks or significant damage.
Are the antibacterial properties of wood lost over time?
The natural antibacterial properties of wood can be diminished if not properly cared for. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and treating with appropriate oils, helps preserve these properties.
What applications do antibacterial woods have?
Woods with antibacterial properties are ideal for:
- Kitchen utensils: Cutting boards, spoons, spatulas.
- Furniture: Tables, countertops, bathroom furniture.
- Coverings: Floors and walls in environments where hygiene is crucial.
Are there treatments that improve the antibacterial properties of wood?
Yes, some treatments and finishes can enhance the antibacterial properties of wood. For example, some manufacturers use advanced technologies that eliminate up to 99.9% of surface bacteria within 24 hours.
Is wood antibacterial?
Yes, various studies have shown that wood has natural antibacterial properties. This is due to the presence of compounds such as tannins and resins, which hinder the survival of bacteria on its surface. Furthermore, its porous structure can encapsulate and isolate microorganisms, reducing their ability to multiply.
Which wood is more antibacterial?
Oak stands out for its high antibacterial efficacy. Studies have shown that oak cutting boards can significantly eliminate harmful bacteria after cleaning. This is attributed to its high tannin content and porous structure, which hinders bacterial growth.
Is the cutting board antibacterial?
Wooden cutting boards, especially those made of oak, walnut, and bamboo, have natural antibacterial properties. These woods can inhibit the growth of bacteria on their surfaces, offering a hygienic option for food preparation.
Is walnut wood antibacterial?
Yes, walnut wood contains tannins that give it antimicrobial properties. This makes it suitable for making kitchen utensils and cutting boards, as it can help inhibit the growth of bacteria on their surfaces.
Are exotic woods antibacterial?
Some exotic woods, such as teak and iroko, possess natural antibacterial properties. However, it’s important to consider that not all exotic woods possess these properties, and some may contain natural oils that are unsafe for food contact.
How effective are wooden cutting boards versus plastic ones?
Wooden cutting boards have been shown to be more effective at inhibiting bacterial growth compared to plastic ones. Studies indicate that bacteria die more quickly on wooden surfaces due to their natural properties, while they can survive and multiply on plastic.
How should wooden cutting boards be cleaned to maintain their antibacterial properties?
It’s recommended to hand-wash wooden boards with warm water and mild soap, dry them completely, and periodically apply mineral oil or specific wood oil. Avoid submerging them in water or putting them in the dishwasher, as excessive moisture can deteriorate the wood and affect its properties.
Is it safe to use wooden cutting boards for all types of foods?
Yes, wooden boards are safe for cutting various types of food. However, it’s recommended to use separate boards for raw meats and other foods to avoid cross-contamination, and be sure to clean them properly after each use.
What are the differences between hardwoods and softwoods in terms of antibacterial properties?
Hardwoods, such as oak and walnut, typically have a higher density and tannin content, giving them better antibacterial properties compared to some softwoods.
Is it advisable to use wooden cutting boards in humid environments?
Wood can absorb moisture, which could affect its durability. However, with proper maintenance and ensuring complete drying after each use, wooden boards can be used in humid environments without problems.
Are the antibacterial properties of wood sufficient to guarantee food safety?
While wood has natural antibacterial properties, it is essential to complement them with good hygiene practices, such as proper cleaning and using separate boards for different types of food, to ensure food safety.
Otras entradas del blog

Olive Wood: Uses and Characteristics

Healthiest Cutting Board: Why End Grain Boards Are Superior

White wood: Common Species and Uses

IPE Wood: Uses and Characteristics
Nuestras tablas de cortar:

Linea
Cherry cherry cutting board
Linea
Cherrycherry cutting board

Linea
Maple grain maple board
Linea
Maplegrain maple board

Calida
end grain cutting board

ARGILLA
long charcuterie board








